
A Brief History of the U.S. Navy Medical Corps
The U.S. Navy Medical Corps has a history that evolves from a humble beginning during the Revolutionary War to its current role as a vital component of modern military medicine. The Medical Corps ensures the health and well-being of sailors, Marines, and their families, while contributing to public health and advancements in medical science.
Origins in the Revolutionary War
The roots of Navy medicine trace back to the Revolutionary War, when medical care aboard ships was primitive at best. Shipboard surgeons, often lacking formal medical training, treated injuries and disease with the limited tools and knowledge available to them. In the early days of the U.S. Navy, physicians served without formal commissions, often receiving temporary appointments for specific cruises. Their primary tasks included amputations, treating infections, and caring for diseases like scurvy and dysentery.
In 1798, Congress formally established the Department of the Navy, creating the foundation for organized medical care within the naval service. Surgeon Edward Cutbush published the first American text on naval medicine in 1808. The Naval Hospital Act of 1811 marked another milestone, authorizing the construction of naval hospitals to support the growing fleet.
Establishment of the Navy Medical Corps (1871)
The U.S. Navy Medical Corps was officially established on March 3, 1871, by an act of Congress. This legislation created a formal medical staff to support the Navy, setting standards for the recruiting and training naval physicians. These physicians were initially known as “Surgeons” and “Assistant Surgeons,” tasked with providing care on ships and at naval hospitals. The act granted Navy physicians rank relative to their line counterparts, acknowledged their role as a staff corps, and established the title of “Surgeon General” for the Navy’s senior medical officer.
During this period, the Navy Medical Corps began to expand its scope. It embraced emerging medical technologies and scientific discoveries, setting the stage for its later contributions to public health and medical innovation.
The Navy Hospital Corps
The U.S. Navy Hospital Corps was established on June 17, 1898. Its creation was prompted by the increased medical needs during the Spanish-American War. Since then, the enlisted corpsmen have served in every conflict involving the United States, providing critical medical care on battlefields, aboard ships, and in hospitals worldwide.
Corpsmen are trained to perform a wide range of medical tasks, including emergency battlefield triage and treatment, surgery assistance, and disease prevention. They are often embedded directly with Marine Corps units, making them indispensable on the battlefield.
The Hospital Corps is the most decorated group in the U.S. Navy. To date, its members have earned numerous high-level awards for valor, including: 22 Medals of Honor, 182 Navy Crosses, 946 Silver Stars, and 1,582 Bronze Stars.
World Wars and the Expansion of Military Medicine
Both World War I and World War II were transformative for the Navy Medical Corps. During World War I, Navy medical personnel treated injuries and illnesses both aboard ships and in field hospitals. Their efforts were instrumental in managing wartime epidemics, including the devastating 1918 influenza pandemic.
World War II brought further advancements. The Navy Medical Corps played a pivotal role in addressing the challenges of warfare in diverse climates, including tropical diseases in the Pacific Theater. It also pioneered methods for treating trauma, burns, and psychiatric conditions.
Cold War Era and Modernization
The Cold War era marked a time of significant innovation for the Navy Medical Corps. The establishment of the Navy Medical Research Institutes advanced studies in areas such as tropical medicine, submarine medicine, and aerospace medicine. These efforts supported the Navy’s global missions and contributed to broader medical advancements.
In the latter half of the 20th century, Navy medical personnel became key players in humanitarian missions, responding to natural disasters and providing aid in conflict zones. Their expertise in public health, infectious disease control, and trauma care enhanced the Navy’s ability to spread goodwill worldwide.
Modern Contributions and Future Challenges
Today, the Navy Medical Corps supports both military readiness and global health. Its personnel provide care on ships, submarines, aircraft carriers, and for Marine Corps forces, and at shore-based facilities. They also participate in humanitarian missions and disaster response, reflecting the Navy’s commitment to a broader vision of security and well-being.
In recent years, Navy medicine has faced challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic, addressing mental health issues among service members, and adapting to emerging threats like climate change and cyber warfare defense. These challenges underscore the evolving role of the Navy Medical Corps in a complex world.
From its early days of rudimentary care to its modern role in global health and innovation, the U.S. Navy Medical Corps has been a cornerstone of military medicine. Its contributions extend beyond the battlefield, shaping public health, medical research, and humanitarian efforts worldwide.
As the Navy Medical Corps continues to adapt to new challenges, it remains a testament to the enduring value of medical service in the defense of the nation and the promotion of global health.








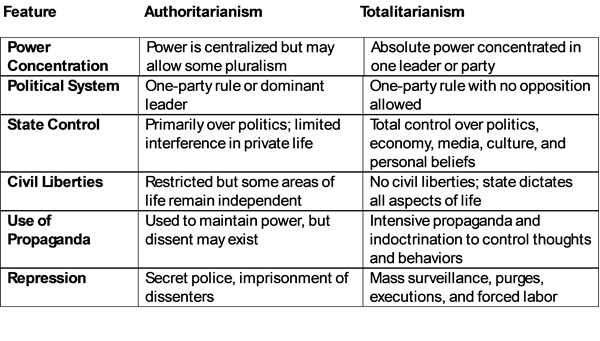



What Is Fascism Anyway?
By John Turley
On March 29, 2025
In Commentary, History, Politics
Fascist! The very word conjures up images of totalitarianism, militarism, suppression of dissent and brutality. Unfortunately, it’s become a ubiquitous portion of our political discourse. Each side, at one time or another, has accused the other of being fascist. But what do they really mean by fascist? Do they understand the definition and the reality of fascism? Or do they simply mean: “I disagree with you, and I really want to make you sound evil.”
I decided I needed to know more about fascism, so I’ve done some research, and I’d like to share the results with you. As I frequently do, I’ll start with the dictionary definition. According to Merriam-Webster fascism is a political philosophy, movement, or regime that exalts nation and often race above the individual and that stands for a centralized autocratic government headed by a dictatorial leader, severe economic and social regimentation, and forcible suppression of opposition.
As with many dictionary definitions, it gives us the 50,000-foot view without any real detail. What I’d like to do is cover the origins of fascism, its basic principles and how it rose to prominence in the middle of the 20th century. I also want to compare fascism to communism—another ideology that shaped much of the 20th century—and to provide insights into the differences and similarities between these two systems.
The Origins of Fascism
Fascism emerged in the early 20th century, primarily in Italy, as a reaction to the perceived failures of liberal democracy and socialism. The term itself comes from the Italian word “fascio,” meaning a bundle or group, symbolizing unity and collective strength. It also references fasces, a bundle of rods tied around an ax symbolizing authority in the Roman Republic. It was appropriated as a symbol by Italian fascists in an attempt to identify with Roman history, much as American patriotic symbols are being appropriated by the radical right in the U.S. today.
Benito Mussolini, an Italian political leader, is often credited as the founder of fascism. He established the groundwork for first fascist regime in Italy beginning in 1922 after he was appointed Prime Minister. Fascism arose in a period of social and economic turmoil following the First World War. Many people in Europe were disillusioned with the existing political systems, which they believed had failed to prevent the war and its devastating consequences. The post-war economic instability, along with fears of communist revolutions like the one in Russia, provided fertile ground for the rise of fascist movements.
Moussolini, together with Italian philosopher Giovanni Gentile, published “The Doctrine of Fascism” (La Dottrina del Fascismo) in 1932, after he had consolidated political power in his hands. It lays out the guiding principles and theoretical foundations of fascism, stressing nationalism, anti-communism, the glorification of the state, the belief in a strong centralized leadership, and the rejection of liberal democracy.
The Philosophical Basis of Fascism
Fascism is rooted in several key philosophical ideas:
Implementation and Practice of Fascism
Fascism has been implemented in various forms, with Italy under Mussolini and Nazi Germany under Adolf Hitler being the most prominent examples. In practice, fascist regimes are characterized by:
Comparing Fascism and Communism
While both fascism and communism reject liberal democracy, they differ significantly in their goals and methods.
Comparative Examples
Conclusion
Fascism and communism, despite their profound differences, share certain similarities in practice, particularly in their authoritarianism and intolerance of dissent. However, their philosophical foundations and goals are fundamentally different: fascism seeks to elevate the nation above all else, while communism theoretically aims to create a classless society. Understanding these ideologies and their historical manifestations is crucial for anyone interested in the political history of the 20th century and its lasting impact on the world today.
We can use our understanding of fascism and its comparison to democracy to ask important questions. What kind of government do we want? Are there any possible crossovers or compromises between the two? And, importantly, should there be?
Postscript
Many of the ideas in this post were inspired by two excellent books on the subject, “The Origins of Totalitarianism” by Hannah Arendt and “Fascism: A Warning” by Madeleine Albright.